A Quick Guide
Over the years, different psychologists have given different theories to explain emotions, their origin, and their function in our life. Dr. Albert Ellis, an important figure in Rational Emotive Behavior Theory, gave the ABCDE theory of emotions. You can apply this theory to your own emotional experiences to understand them better. This will help you be more aware and mindful of your thoughts, emotions, bodily reactions, and specific triggers.
The ABCDE theory of emotions
According to Dr. Albert Ellis, an emotional experience can be broken down into multiple parts. These are
- A= Activating Event
- B= Beliefs
- C= Consequence
- D= Dispute
- E= Effect
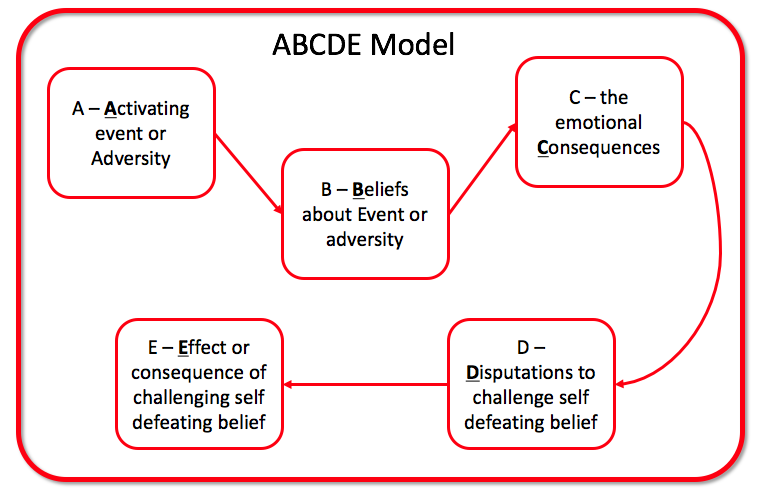
A= Activating Event
Activating event simply refers to an external stimulus or some change in the environment that triggers the emotional response.
For example, failing an exam
B= Beliefs
People believe that these external events are the reason for their negative emotions. In short, they blame their problems on the event. Whereas it is not the event itself but a person’s beliefs that lead to negative emotions. This explains why different people have different responses to the same event. For example, one person may perceive having a child as the biggest blessing of his life. Whereas another may blame the child for tying him down. Etc. So basically our beliefs or perception of the event determines our negative feelings.
C= Consequence
The consequence refers to the emotional outcome as a result of your beliefs. For example, you may feel depressed, angry, anxious, happy, etc. Usually, we tend to blame the activating event. For instance, ‘I am anxious because of the big exam’. Whereas in reality, you may be anxious because you believe you are incompetent and will fail the exam. So our thoughts play a dominant role here. When people blame the activating event, they just end up believing their beliefs and feel worse. Such that they don’t go to the next stage.
D= Dispute
In this stage, we raise questions or dispute our thoughts/beliefs about the event. This can include questioning the validity of our rational and irrational thoughts.
For example, How likely it is that I will fail the exam even though I have completed the preparation?
E= Effect
This refers to how we rationally approach a situation after our mind and body are relatively relaxed.
Applying ABCDE theory of emotions _ An example
- A= Activating Event: Not getting a call after a job interview
- B= Beliefs: I am incompetent which is why they must have rejected me.
- C= Consequence: Feeling depressed
- D= Dispute: Did I really get rejected because I am not qualified? Do I know this for sure? Could there be other reasons?
- E= Effect: Deciding to call the company to check the status of the interview. Also, applying to other job advertisements as well. Feeling more in control and confident as a result.
Applying the ABCDE theory of emotions to daily life
Just like suggested above, start applying the ABCDE theory to your own life. Objectively analyze your experiences, and question the validity of your effect and beliefs. Accordingly, try to adopt healthier thoughts. Doing so on a frequent basis will help you to change the maladaptive beliefs and adopt healthier ones.
Watch: [ABC model of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy]
We hope you found this article useful in understanding more about the theory of emotions. To learn more about emotional awareness, check out our other article: How To Become Aware Of Your Emotions.



 The Transformative Power of Meditation on Mental Health
The Transformative Power of Meditation on Mental Health  Understanding the Chaotic Mind: Navigating the Intricacies of Cognitive Complexity
Understanding the Chaotic Mind: Navigating the Intricacies of Cognitive Complexity  Understanding the Emotional Mind, Rational Mind, and Wise Mind
Understanding the Emotional Mind, Rational Mind, and Wise Mind  The Emotional Mind: Unraveling the Complex Web of Emotions
The Emotional Mind: Unraveling the Complex Web of Emotions  Understanding the emotions behind your behavioral patterns
Understanding the emotions behind your behavioral patterns  Understand the body language of emotions
Understand the body language of emotions