A Quick Guide
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), also known as shock therapy, is a safe procedure used for severe mental illnesses when standard treatments are ineffective. It involves inducing a seizure through a brief electric current under anesthesia. ECT can be beneficial for severe treatment-resistant depression, severe mania in bipolar disorder, and certain forms of schizophrenia. However, it carries risks such as short-term memory loss and side effects associated with anesthesia.
What is Electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy also known as shock therapy is a procedure that is done on people with severe mental illness. Contrary to popular belief instilled in us by the media, electric therapy is quite a safe procedure. Mostly if a person is not getting better by the standard treatment of their respective illnesses then they can opt for ECT. It has proven to be quite beneficial in reversing their symptoms.
ECT is done by inducing a brief electric current that results in a seizure. This is done under proper anesthesia so the patient does not feel any pain whatsoever. A number of trained mental health professionals perform ECT. This includes an anesthesiologist, a psychiatrist, a physician assistant, or a nurse. They see to it that the procedure is being done safely and has minimal side effects.
Of course, there are certain myths that date back to the history of shock therapy. The procedure was initially used during the 1940-1950 era, but there was no concept of informed consent back then. Mental health professionals were not as trained. There were no proper ethical considerations. The procedure was also administered incorrectly. Though today we have overcome all these issues.
Steps before ECT
Before any procedures are done, the patient is supposed to give informed consent to the treatment. You have to consult your psychiatrist about the possible benefits and risks of the treatment. In case, a patient is too ill to give their own consent, then the consent process will be governed by the state law, for instance, by a court-appointed guardian.
Typically before the procedure, your doctor will have your complete psychiatric assessment. You will also have to get several tests done such as blood and urine tests, along with Xrays and CT scans of your skull brain, and spine. You may also have to get an Electrocardiogram (ECG) to take a look at your heart’s electrical system.
The procedure of ECT
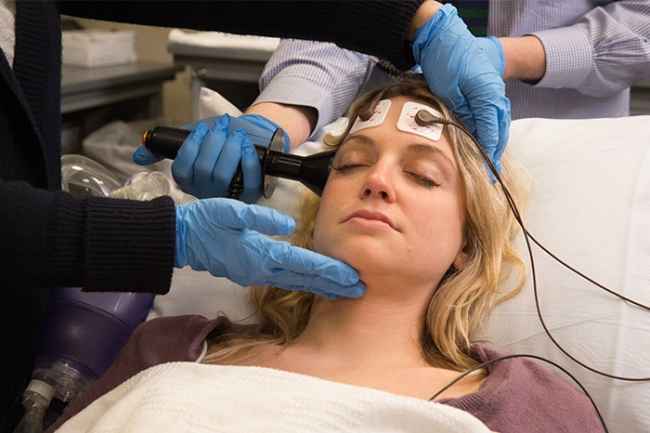
Your doctor will give you specific instructions before the procedure. Initially, You will be given general anesthesia and put to sleep. Next, you will have a short physical examination to check the functioning of your heart and lungs. Then you will have an intravenous line (IV) inserted, so you can be provided with medication and fluids. After the basic preparation has been done. You will have electrodes attached to specific areas of your scalp. Then very brief and controlled electrical currents will be passed into your brain which will cause a seizure that would last for 1 minute.
You will stay asleep throughout the ECT and will wake up after about 10 to 15 minutes. You may experience some confusion but that is common. Usually, you get ECT about 2 to 3 times a week. There are up to a total of 12 sessions depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Watch: [ECT Electroconvulsive Therapy – WVU Medicine Health Report]
Pros and Cons
Before opting for this procedure, you should know about the pros and cons of shock therapy. Usually, the procedure is done if the patient has suicidal tendencies and the standard treatment is not working for them.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ECT is extremely effective more so than any other procedure available. | There is a small risk of short-term memory loss. |
| ECT is quite a safe procedure today. | There are risks involved with general anesthesia such as headache, fatigue, confusion, or nausea. |
| It works quite quickly than other treatments. | ECT is a medically intensive procedure so it is not readily available at smaller healthcare facilities. |
| It is most effective when combined with medication. | It may result in a loss of emotional responses. |
What ECT can help with?
ECT can be extremely beneficial in some cases such as:
Severe treatment-resistant depression: If no medication and therapy is working and the person has lost touch with reality (also known as psychosis). Or if they are moving towards suicidal tendencies.
Severe mania: If a person has bipolar with severe symptoms, then ECT can be effective for them.
Schizophrenia: People with catatonic behavior (lack of speech and movement) or those with other psychotic disorders can get ECT.
You should always make an informed decision regardless of whatever procedure you are opting for.
We hope you found this article useful in understanding Electroconvulsive therapy, why it’s done, the steps before and after the procedure, and its pros and cons.